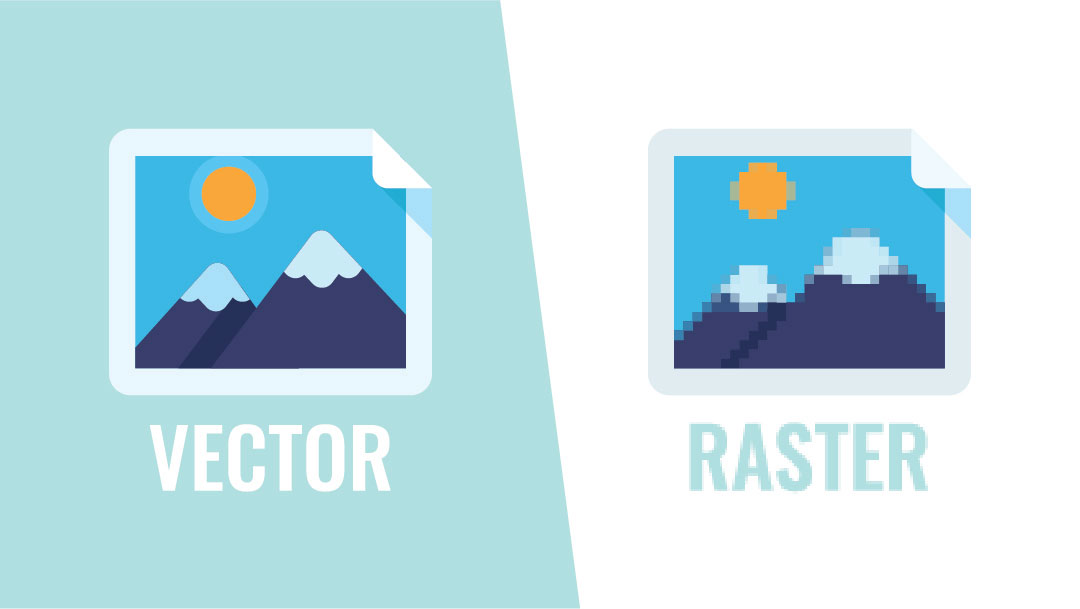
Understanding the distinction between vector and raster graphics is crucial in graphic design and printing. Clients often encounter these terms when collaborating with printers or design agencies like Adams Media Group. This article aims to clarify the definitions, differences, and practical applications, empowering you with the knowledge necessary for effective collaboration.
What is a Vector Graphic?
Vector graphics are defined by mathematical equations that delineate geometric shapes like lines, curves, and polygons. Unlike raster graphics, which utilize pixels, vector graphics are resolution-independent. This quality allows them to be scaled infinitely without sacrificing quality. Standard vector file formats include .ai (Adobe Illustrator), .eps (Encapsulated PostScript), and .svg (Scalable Vector Graphics).
Benefits of Vector Graphics:
- Scalability: Vector graphics can be resized without loss of clarity, making them ideal for large-format printing and resizing for various applications.
- Editability: Vector files are composed of editable paths and shapes, facilitating easy modifications of colors, shapes, and sizes.
- Compact File Sizes: Vector files generally have smaller sizes than raster files, making them easier to store, transfer, and manipulate.
Common Uses of Vector Graphics:
- Logos and Branding: Ideal for creating logos and brand elements requiring consistent appearance across diverse media and sizes.
- Icons and Illustrations: Vector graphics are used extensively in icons, illustrations, charts, and diagrams, where precision and adaptability are paramount.
- Print Media: Due to their clarity and versatility, vector graphics are preferred for printed materials such as business cards, brochures, banners, and posters.
What is a Raster Graphic?
Raster graphics, or bitmaps, are composed of a grid of pixels, each assigned a specific color or shade. Popular raster file formats include .jpg, .png, .gif, and .bmp. Unlike vector graphics, raster graphics are resolution-dependent, meaning they can lose quality when scaled up or down.
Characteristics of Raster Graphics:
- Resolution Dependence: Enlarging a raster graphic beyond its original size can lead to pixelation and a decline in image quality.
- Photorealism: Well-suited for photographs and images with intricate details and color gradients.
- Larger File Sizes: Raster files may have larger sizes due to the quantity of pixel data they contain.
Common Uses of Raster Graphics:
- Photography: Raster graphics are commonly used for digital photographs and camera images.
- Web Graphics: Raster graphics are suitable for web banners, social media posts, and digital advertisements due to their detail and color depth.
- Complex Artwork: Raster graphics are frequently used for digital paintings, detailed illustrations, and multimedia projects requiring intricate visuals.
Why Vector and Raster Graphics Matter in Branding
At Adams Media Group, we recognize the importance of delivering comprehensive branding guidelines that include vector and raster graphics. Vector graphics ensure your brand maintains consistency and sharpness across various mediums and sizes, while raster graphics provide the necessary detail and realism for digital and print applications. Our branding guidelines equip you with all file versions and sizes for seamless implementation across diverse platforms, from print materials to digital assets and social media avatars.
Understanding the differences between vector and raster graphics empowers you to make informed decisions when collaborating with printers, designers, and digital marketers. At Adams Media Group, we’re committed to delivering high-quality design solutions tailored to enhance your brand identity. Contact us today to learn more about how we can elevate your brand with our comprehensive design services, including customized branding guidelines that cater to your unique needs.